Smith & Nephew Iodoflex Iodine Gel Pad Features
- Effective antimicrobial.
- Exudate and debris are removed effectively.
- A change in color (white) indicates when IODOFLEX should be changed.
- Gel formed over the wound promotes moist healing.
- Accelerated healing rates can lead to earlier patient discharges
- Comes with Cadexomer iodine which can absorb up to 6 times its weight in fluid.
- Range of sizes to suit most wound sizes.
- IODOFLEX is non-adhesive which can reduce trauma at dressing changes and encourage patient compliance.
When to use Iodoflex Cadexomer Iodine Gel Pad?
IODOFLEX Pads - For use in treating wet ulcers and wounds such as
Contraindications / Precautions
IODOFLEX is contraindicated in:
- Patients with known or suspected iodine sensitivity
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis
- Non-toxic nodular goitre
- Children
- Pregnant or lactating women
Special Warnings and Precautions for Use
- Iodine may be absorbed systemically, especially when large wounds are treated. Patients with severely impaired renal function or a past history of any thyroid disorder are more susceptible to alterations in thyroid metabolism with chronic IODOFLEX therapy. In endemic goitre, there have been isolated reports of hyperthyroidism associated with exogenous idoine. It has been observed occasionally that an adherent crust can form when IODOFLEX is not changed with sufficient frequency.
What to buy with Iodoflex Dressing
How does Cadexomer Iodine work?
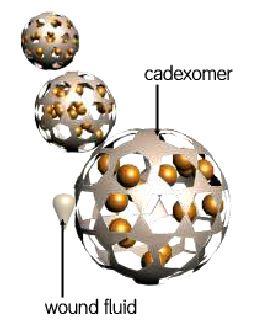
Cadexomer Iodine is a uniquely formulated starch matrix formed into spherical, highly absorbent microbeads containing 0.9% elemental iodine. The Cadexomer is a 3D cross - linked polysaccharide starch matrix. The 0.9% iodine is physically bound to the Cadexomer matrix and is only released when it is required. Wound fluid and exudate are absorbed into the Cadexomer beads of the Cadexomer Iodine, allowing the iodine to be released slowly.
When Cadexomer Iodine is applied to the wound surface, exudate, pus and debris are absorbed into the Cadexomer beads. The beads will swell resulting in the formation of a demonstrable gel. The presence of exudate and the consequent swelling of the beads results in the cross-linked bonds of the Cadexomer matrix breaking and the iodine being released into the surrounding wound environment.
When the iodine is released, the amount of iodine released will be to a level such that the concentration of iodine in the dressing and the wound environment reach equilibrium. The equilibrium will remain and no further iodine will be released until the balance is disturbed. Once the iodine in the surrounding wound environment has been depleted, more will be released from the product until the equilibrium is reached again and will remain until disturbed. This process will continue until all the 0.9% iodine within the product has been exhausted.
How to use Smith & Nephew Iodoflex Iodine Gel Pad Dressing?
Step 1 – Application
- Clean the wound and the surrounding area with either a gentle stream of sterile water or saline. DO NOT DRY the wound surface.
- Remove the carrier gauze on both sides of the paste using aseptic technique.
- Apply IODOFLEX dressing to the wound surface. Apply compression bandaging when appropriate. Any remaining IODOFLEX should be discarded.
Step 2 – Changing
- IODOFLEX dressing should be changed when it has become saturated with wound fluid, indicated by loss of colour, usually two to three times a week. If the wound is discharging heavily, daily changes may be needed.
- If necessary, soak the dressing for a few minutes.
- Gently remove the IODOFLEX using a stream of sterile water or saline.
- Gently blot any excess fluid, leaving the wound surface slightly moist, before re-applying IODOFLEX.
Step 3 –After Using IODOFLEX
- IODOFLEX may cause smarting especially in the first hour after treatment. Occasionally, IODOFLEX may cause the skin around the wound edges to redden. If the symptoms persist, or you experience other symptoms, please contact your doctor or nurse.
Related Articles
{{x.ShortDescription}} ...
Share
Customer Reviews
Ratings & Reviews
5.0
★ ★★ ★★ ★★ ★★ ★
2 Authentic Reviews

Write a Review★★★★★
Charles T. | 5 years ago
This review was originally written for Smith & Nephew Iodoflex Sterile Cadexomer Iodine Gel Pad Dressing
The product works very good in healing an existing decubitus ulcer on the patients right hip. Changed every 2 days as it breaks down and changes color.
Eliz J. | 7 years ago
This review was originally written for Smith & Nephew Iodoflex Sterile Cadexomer Iodine Gel Pad Dressing
Very good savings buying here.